Continuous availability is a design methodology that provides uninterrupted access to application services and data. Critical business applications built using this methodology are always on and available. At a minimum, the components in an application service stack are built to a 2N design specification; that is two times the Need in parallel with both sets of the Need actively being used. 2N application designs can tolerate the loss of a site, server, or infrastructure service without need for failover mechanisms or recovery operations. The approach leverages a multi-site active/active infrastructure, object brokers, and advanced storage virtualization technology to deliver a higher level of service availability than previously possible, while reducing costs and simplifying administration…
![]() PowerM Solution : EMC VPLEX and EMC RecoverPoint
PowerM Solution : EMC VPLEX and EMC RecoverPoint
1. Evolving client requirement:
Continuous availability architectures and processes are used by forward-thinking organizations that seek to ensure exceptionally high levels of service availability for mission- and business-critical applications. Two factors are driving this migration to continuous availability solutions. The first is the escalating demand for uninterrupted availability of key business applications, as consumers and markets have come to expect that services will be accessible anytime, from anywhere, without exception. In this context, the costs of even brief outages can be severe.
The second driver is the shortcomings of conventional approaches to the availability challenge, which is to pair separate and distinct systems and processes for high availability and disaster recovery using N+1 designs. Following conventional approaches, critical applications are architected using N+1+1 designs, that is, they are built with a Need plus one spare methodology (+1, within a single site) and disaster recovery (+1 again across primary and backup sites). And typically since the spares are passive, some sort of failover or recovery operation needs to take place to bring the spare online resulting in needless downtime.
Continuous availability is made possible by technology advances that make it feasible and economical to build and maintain multi-site active/active architectures for business applications. Rather than having costly resources idling in passive mode, continuous availability topologies efficiently “stretch” active assets across two or more sites.
The main elements of a continuous availability architecture are:
- Two or more data centers deployed in active/active mode, each with a complete set of infrastructures that have no single point of failure. The sites need to be far enough apart to not both be impacted by a single disaster, but close enough to allow for synchronous data mirroring across sites. Depending on regional location, between 25 and 60 miles apart is ideal.
- An advanced distributed data virtualization layer such as EMC VPLEX Metro to synchronously mirror and maintain data coherency across sites.
- Business applications architected to run in continuous availability mode using scale-out clustering with DB solutions like Oracle RAC or clustered file systems from VMware. Oracle RAC and VMware’s VMFS file system act as object brokers to enable coherent simultaneous updates to data that is read/write in both sites.
- A transaction distribution mechanism to balance transaction loads across the active/active sites during normal operations, and to route all traffic to the good site in the event that disaster or maintenance activity takes a site down.
2. EMC VPLEX
EMC VPLEX represents the next-generation architecture for data mobility and information access.VPLEX is a solution for federating EMC and non-EMC storage. VPLEX resides between the servers and heterogeneous storage assets and has unique characteristics in its architecture:
- Scale-out clustering hardware lets you start small and grow big with predictable service levels
- Advanced data caching utilizes large-scale SDRAM cache to improve performance and reduce I/O latency and array contention
- Distributed cache coherence provides automatic sharing, balancing, and failover of I/O within and between VPLEX clusters
- A consistent view of one or more LUNs between VPLEX clusters separated either by a few feet within a data center or across asynchronous RTT distances enables new models of high availability, workload mobility, and collaboration.
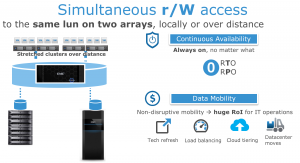
Figure 1 : VPLEX Simultaneous R/W Access
3.EMC RecoverPoint
Dell EMC RecoverPoint provides continuous data protection for comprehensive operational and disaster recovery. RecoverPoint delivers benefits including the ability to:
- Enable Continuous Data Protection for any PiT recovery to optimize RPO and RTO
- Ensure recovery consistency for interdependent applications
- Provide synchronous (sync) or asynchronous (async) replication policies
- Snap-Based replication
- Reduce WAN bandwidth consumption and utilize available bandwidth optimally
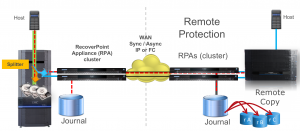
Figure 2 : RecoverPoint continuous data protection
4. Use Case : Banking Customer Morocco
Business Need:
- Enhance RPO and RTO
- Compliance with the Disaster Recovery Plan
- Reduce complex administration task
- Reduce total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Reduce Batch processing time
- Homogeneous virtualization and replication for all high end storage
Challenge:
- Virtualization of existing IBM Storage (XIV Gen1, XIV Gen2, DS48000) and EMC (VMAX 100K)
- Short migration windows
- Flexible RPO and RTO per application / storage subsystem
- Continuous data protection with multiple recovery points to restore applications instantly to a specific point in time
- Tape and backup migration from IBM ProtectTier/IBM LTO Tape Library TS to EMC DataDomain
- Reduce replicated data over the network.
Benefits:
- The solution provides protection to applications in the face of disasters through automatic failover and failback between arrays and datacenters.
- The storage virtualization gives the IT staff much more flexibility to move workloads between different tiers of storage including IBM DS4800, EMC VMAX 100K, and IBM XIV GEN1 and GEN2
- Flexible Deployment: Data migration was done with minimum downtime, saving countless weekends of maintenance downtime and IT resources.
- Minimize network utilization with bandwidth compression and deduplication, significantly reducing replicated data over the network.

Figure 3 : Use case configuration.
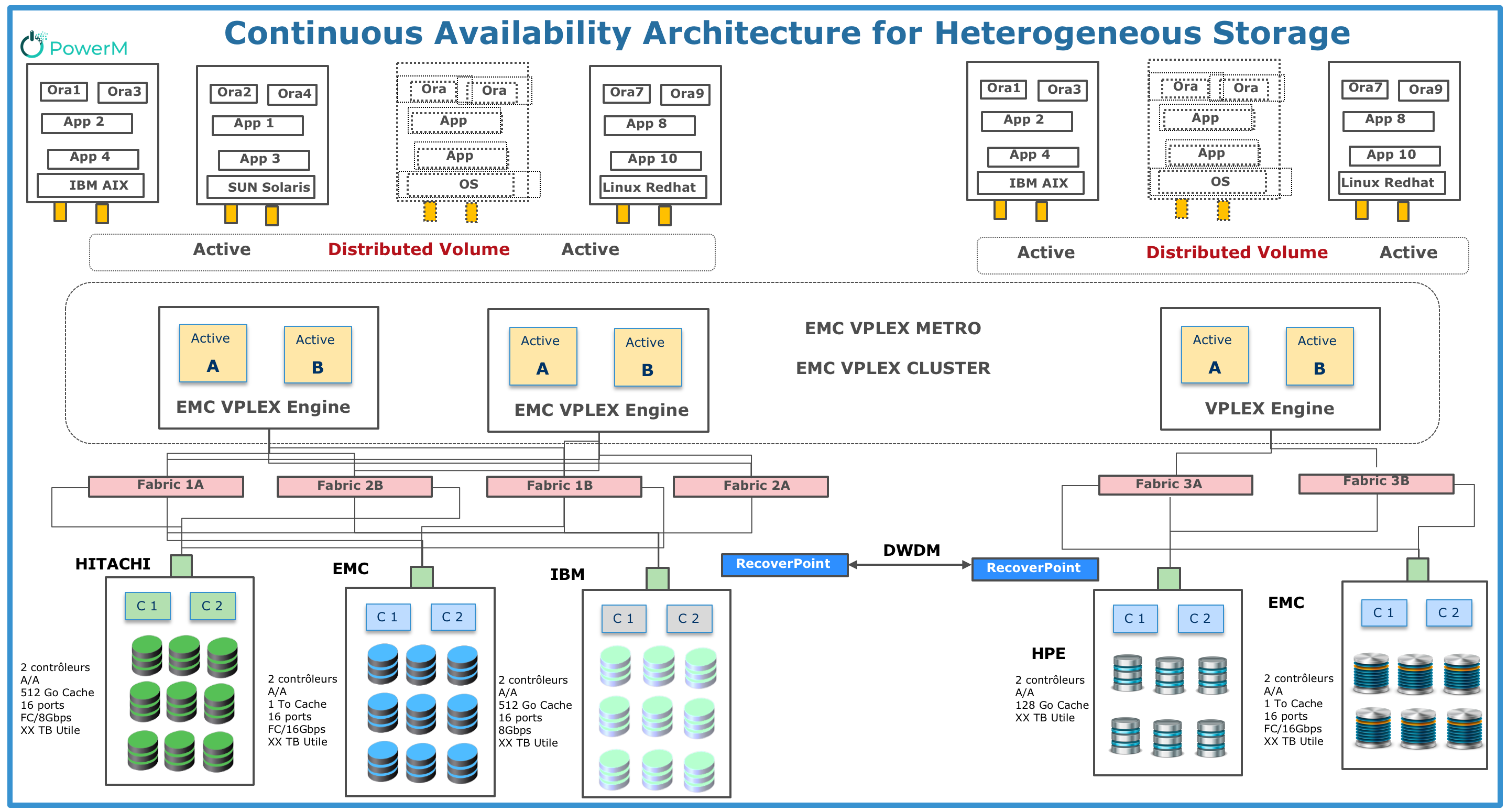
5. Detailed reference architecture:
Need more information about this reference architecture? Send us email : [email protected]
6. Reference:
- DELL EMC Glossary CONTINUOUS AVAILABILITY
- EMC VPLEX Administration Guide
- EMC VPLEX Overview and General Best Practices Guide

